Best CRM for Small Business: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Why Small Businesses Need a CRM
- Key Features to Look for in a CRM
- Top 30 CRMs for Small Businesses in 2025
- 1. HubSpot CRM
- 2. Zoho CRM
- 3. Salesforce Essentials
- 4. Freshsales
- 5. Monday.com CRM
- 6. Pipedrive
- 7. Insightly
- 8. Keap (formerly Infusionsoft)
- 9. Nimble CRM
- 10. Less Annoying CRM
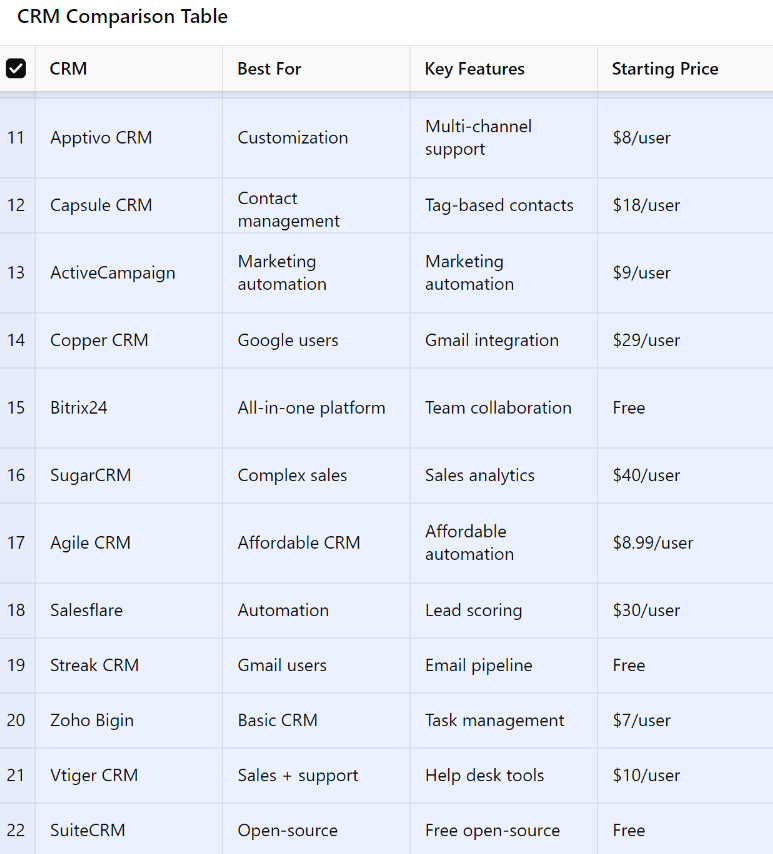
- 11. Apptivo CRM
- 12. Capsule CRM
- 13. ActiveCampaign
- 14. Copper CRM
- 15. Bitrix24
- 16. SugarCRM
- 17. Agile CRM
- 18. Salesflare
- 19. Streak CRM
- 20. Zoho Bigin
- 21. Vtiger CRM
- 22. SuiteCRM
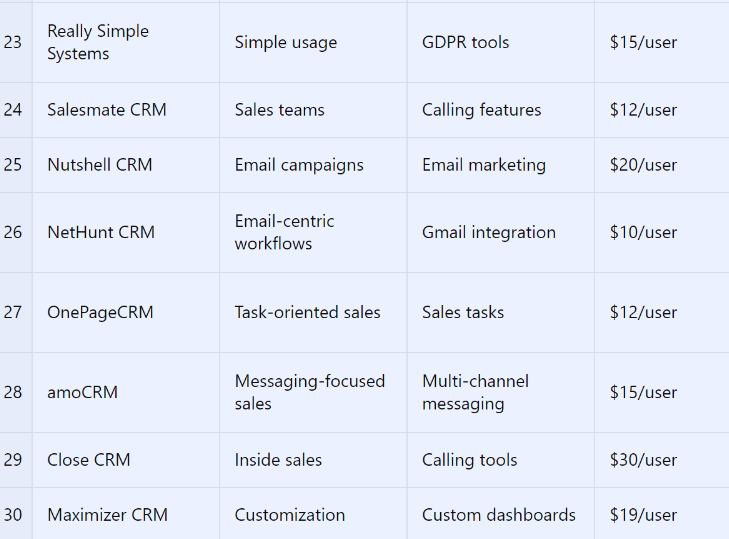
- 23. Really Simple Systems CRM
- 24. Salesmate CRM
- 25. Nutshell CRM
- 26. NetHunt CRM
- 27. OnePageCRM
- 28. amoCRM
- 29. Close CRM
- 30. Maximizer CRM
- Comparison Table of Top CRMs
- How to Choose the Right CRM for Your Business
- Implementation Tips
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of 2025, selecting the best CRM for small business is pivotal for success. A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system streamlines operations, enhances customer interactions, and drives growth. This guide delves into the top 30 CRM solutions tailored for small businesses, providing insights to help you make an informed decision.
Why Small Businesses Need a CRM
Implementing a CRM offers numerous benefits:
- Centralized Information: Consolidates customer data for easy access.
- Improved Customer Relationships: Facilitates personalized interactions.
- Enhanced Productivity: Automates routine tasks, allowing focus on core activities.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides analytics for strategic planning.
Key Features to Look for in a CRM
When evaluating CRMs, consider the following features:
- Contact Management: Efficient storage and retrieval of customer information.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Tracking of sales stages and forecasting.
- Automation: Automated workflows for tasks like follow-ups and data entry.
- Integration: Compatibility with existing tools (e.g., email, calendars).
- Reporting and Analytics: Insights into performance metrics.

Top 30 CRMs for Small Businesses in 2025
Here’s an in-depth look at the top CRM solutions:
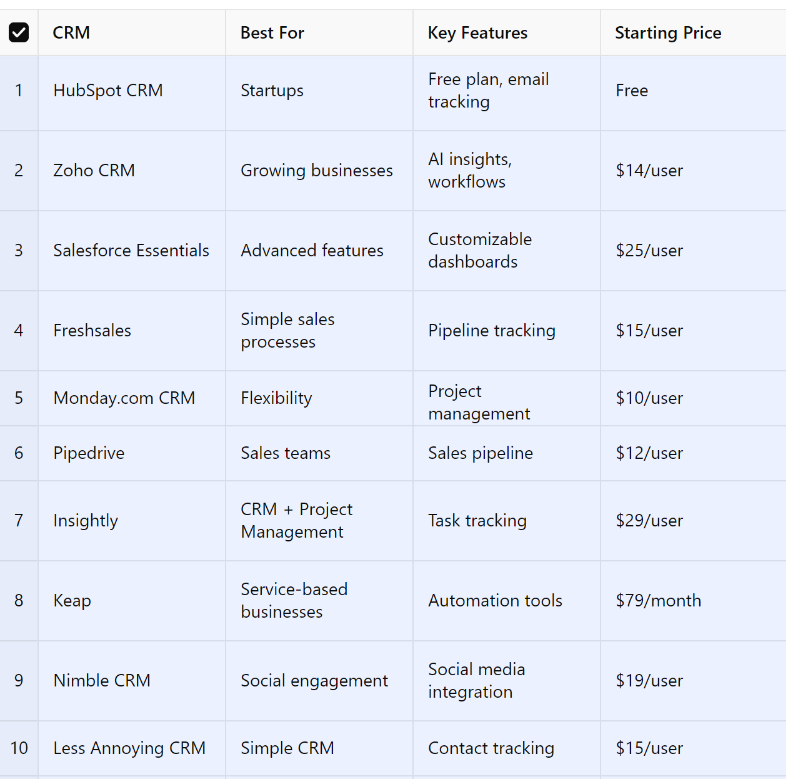
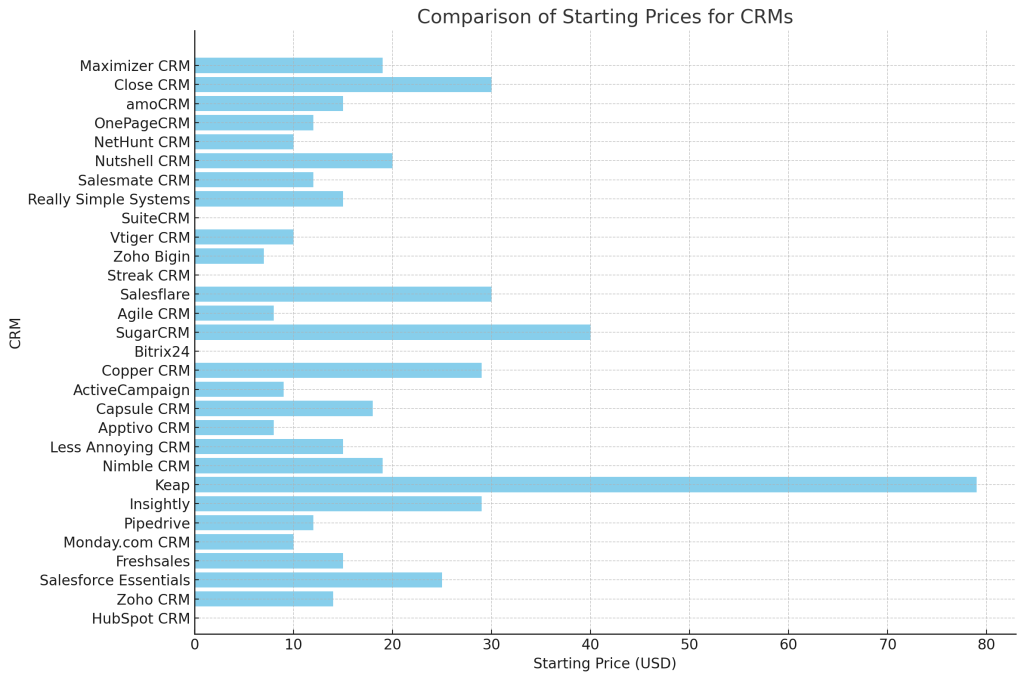
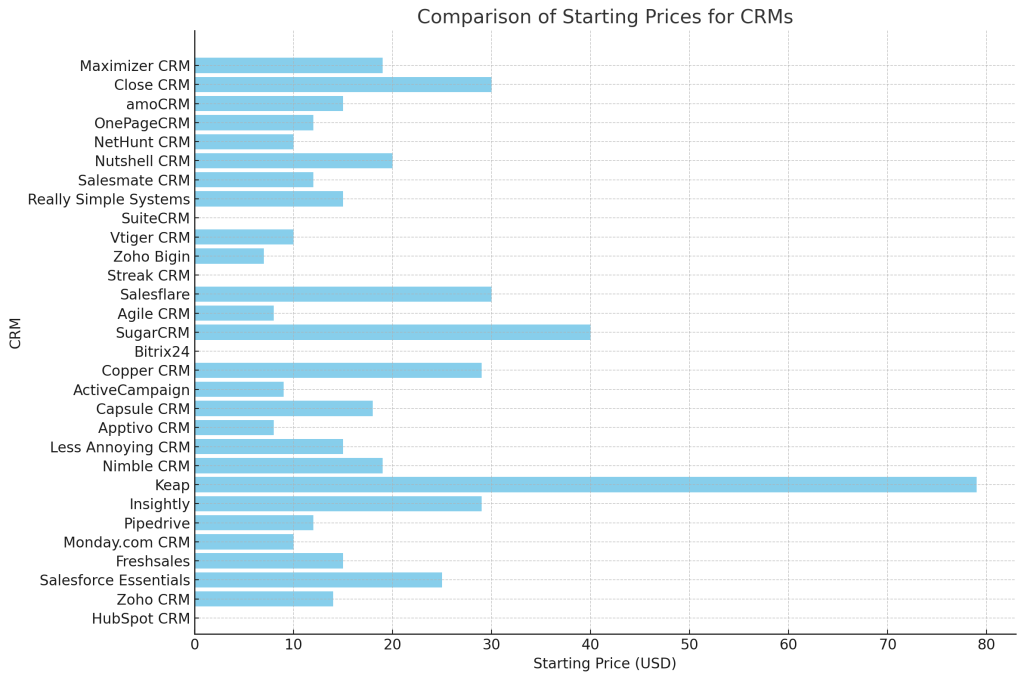
We have created a detailed table comparing all 30 CRMs, highlighting their best use cases, key features, and starting prices. Additionally, the chart visually compares the starting prices to help you make an informed decision.
1. HubSpot CRM
Overview: A free, user-friendly platform with robust features suitable for small businesses.
Key Features:
- Contact and deal management.
- Email tracking and notifications.
- Customizable dashboards.
Pros:
- Free plan with substantial features.
- Seamless integration with HubSpot’s suite.
Cons:
- Advanced features require paid plans.
Ideal For: Startups and small businesses seeking a cost-effective solution.
2. Zoho CRM
Overview: Offers a comprehensive suite with customization and AI-driven insights.
Key Features:
- Workflow automation.
- Multi-channel communication.
- AI assistant for sales predictions.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing tiers.
- Extensive integration options.
Cons:
- May have a learning curve for beginners.
Ideal For: Growing small businesses needing scalability.
3. Salesforce Essentials
Overview: A streamlined version of Salesforce tailored for small businesses.
Key Features:
- Contact and opportunity management.
- Workflow automation.
- AppExchange access for extended functionality.
Pros:
- Highly customizable.
- Robust analytics capabilities.
Cons:
- Higher learning curve.
Ideal For: Small businesses ready to invest in a premium CRM solution with advanced features.
Sources
4. Freshsales
Overview: Part of the Freshworks suite, Freshsales is a powerful CRM that focuses on lead management and automation.
Key Features:
- Built-in phone and email integration.
- AI-powered lead scoring for prioritization.
- Visual sales pipeline for deal tracking.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing and easy setup.
- Intuitive interface suitable for small teams.
- Offers automation for routine sales tasks.
Cons:
- Limited third-party integrations compared to competitors.
Ideal For: Small businesses that need a simple, affordable solution to streamline their sales processes.
5. Monday.com CRM
Overview: Known for its flexibility, Monday.com CRM combines project management and CRM capabilities.
Key Features:
- Customizable workflows and dashboards.
- Automation of repetitive tasks like follow-ups.
- Integration with productivity tools like Slack and Google Workspace.
Pros:
- Highly flexible and visually appealing interface.
- Suitable for diverse industries.
- Easy collaboration for small teams.
Cons:
- Requires setup to tailor workflows to specific needs.
Ideal For: Small businesses needing flexibility in managing projects and customer relationships.
6. Pipedrive
Overview: Pipedrive is a sales-focused CRM designed to help businesses close deals faster.
Key Features:
- Simple, drag-and-drop sales pipeline.
- Email integration and tracking.
- Goal-setting and progress tracking.
Pros:
- Easy to set up and use.
- Focused on sales process efficiency.
- Affordable pricing for small businesses.
Cons:
- Limited functionality beyond sales management.
Ideal For: Small sales teams that need a CRM centered on deal tracking.
7. Insightly
Overview: Insightly combines CRM and project management capabilities in one platform.
Key Features:
- Task and project tracking.
- Custom fields and relationship linking.
- Integration with popular tools like QuickBooks and Xero.
Pros:
- Robust project management features.
- Affordable plans for small teams.
Cons:
- Reporting features can be complex to navigate.
Ideal For: Small businesses needing both CRM and project management in one tool.
8. Keap (formerly Infusionsoft)
Overview: Keap is an all-in-one platform designed for small businesses to manage clients and automate sales.
Key Features:
- Email and text marketing automation.
- Invoice and payment processing.
- Appointment scheduling.
Pros:
- Excellent automation features.
- Combines marketing, sales, and payments in one tool.
Cons:
- Higher pricing compared to other small business CRMs.
Ideal For: Service-based small businesses that need integrated marketing and sales features.
9. Nimble CRM
Overview: Nimble is a social CRM that integrates with social media platforms for customer engagement.
Key Features:
- Social media integration for relationship building.
- Email tracking and analytics.
- Unified contact management.
Pros:
- Focuses on building customer relationships.
- Simple and intuitive interface.
Cons:
- Limited scalability for growing businesses.
Ideal For: Small businesses focused on social media and customer engagement.
10. Less Annoying CRM
Overview: Designed with simplicity in mind, Less Annoying CRM offers straightforward tools for managing customers and sales.
Key Features:
- Contact and lead tracking.
- Basic task management and reminders.
- Simple customization options.
Pros:
- Very affordable pricing.
- Easy to use, even for non-technical users.
Cons:
- Lacks advanced features for scaling businesses.
Ideal For: Small businesses new to CRMs or those looking for a simple, budget-friendly solution.
11. Apptivo CRM
Overview: Apptivo provides a highly customizable and affordable CRM for small businesses.
Key Features:
- Customizable apps for sales, marketing, and invoicing.
- Multi-channel support.
- Mobile CRM for on-the-go management.
Pros:
- Very affordable for its feature set.
- Scalable for growing businesses.
Cons:
- Interface can feel outdated.
Ideal For: Budget-conscious small businesses that want customization.
12. Capsule CRM
Overview: Capsule CRM is a lightweight tool focused on managing relationships and pipelines.
Key Features:
- Task management and sales tracking.
- Contact organization with tags and filters.
- Email integration.
Pros:
- Simple and easy to navigate.
- Affordable pricing.
Cons:
- Limited features compared to more robust CRMs.
Ideal For: Small businesses that prioritize simplicity and contact management.
13. ActiveCampaign
Overview: ActiveCampaign combines CRM and marketing automation in a single platform.
Key Features:
- Advanced marketing automation.
- Email marketing and lead nurturing.
- Sales automation and tracking.
Pros:
- Powerful automation features.
- Integrates well with third-party tools.
Cons:
- More focused on marketing than traditional CRM features.
Ideal For: Small businesses prioritizing email marketing and customer engagement.
14. Copper CRM
Overview: Copper CRM is built specifically for Google Workspace users.
Key Features:
- Seamless integration with Gmail and Google Calendar.
- Task and project tracking.
- Sales pipeline visualization.
Pros:
- Extremely user-friendly for Google users.
- Requires minimal training.
Cons:
- Limited features outside of the Google ecosystem.
Ideal For: Small businesses already using Google Workspace.
15. Bitrix24
Overview: Bitrix24 offers a combination of CRM, project management, and collaboration tools.
Key Features:
- Sales and customer management.
- Team collaboration tools.
- Built-in telephony for calls.
Pros:
- Free plan with robust features.
- All-in-one platform for small teams.
Cons:
- Can feel cluttered due to extensive features.
Ideal For: Small teams looking for an integrated CRM and collaboration tool.
16. SugarCRM
Overview: SugarCRM provides a comprehensive platform for customer management and marketing automation.
Key Features:
- AI-powered predictive insights.
- Sales and marketing automation.
- Advanced reporting and analytics.
Pros:
- Highly customizable for specific business needs.
- Strong customer support.
Cons:
- Higher cost for smaller businesses.
Ideal For: Small businesses with complex sales processes and analytics needs.
17. Agile CRM
Overview: Agile CRM combines contact management with robust marketing and sales tools.
Key Features:
- Email and social media integration.
- Drag-and-drop marketing automation.
- Appointment scheduling and tracking.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing for small businesses.
- Easy-to-use interface.
Cons:
- Limited integrations compared to larger CRMs.
Ideal For: Small businesses seeking an affordable all-in-one solution.
18. Salesflare
Overview: Salesflare is designed for small B2B businesses focused on selling more with less manual input.
Key Features:
- Automatic data entry for contact management.
- Email and social media tracking.
- Pipeline management.
Pros:
- Easy to set up and use.
- Minimal manual data entry.
Cons:
- Limited customization options.
Ideal For: Small sales teams that need automation and efficiency.
19. Streak CRM
Overview: Streak is a CRM built directly into Gmail for seamless integration with email.
Key Features:
- Email pipeline management.
- Collaboration tools within Gmail.
- Task and project tracking.
Pros:
- Works entirely within Gmail.
- No need for separate software.
Cons:
- Limited features for complex workflows.
Ideal For: Gmail users looking for a lightweight CRM solution.
20. Zoho Bigin
Overview: Zoho Bigin is a simplified version of Zoho CRM, tailored for very small businesses.
Key Features:
- Contact and pipeline management.
- Email tracking and task automation.
- Mobile app for on-the-go access.
Pros:
- Extremely affordable.
- Simple and beginner-friendly.
Cons:
- Limited scalability for growing businesses.
Ideal For: Small businesses or freelancers needing a basic CRM.
21. Vtiger CRM
Overview: Vtiger CRM offers an all-in-one platform for customer support, sales, and marketing.
Key Features:
- 360-degree customer view.
- Email campaigns and automation.
- Help desk and ticketing features.
Pros:
- Integrated help desk tools.
- Comprehensive customer insights.
Cons:
- Slightly outdated interface.
Ideal For: Small businesses requiring both sales and customer support tools.
22. SuiteCRM
Overview: SuiteCRM is an open-source CRM offering extensive customization options.
Key Features:
- Advanced reporting and dashboards.
- Workflow automation.
- Free and open-source software.
Pros:
- No licensing fees.
- High level of customization.
Cons:
- Requires technical knowledge for setup.
Ideal For: Small businesses with technical resources to customize a CRM.
23. Really Simple Systems CRM
Overview: A lightweight CRM focused on ease of use and simplicity.
Key Features:
- Sales and pipeline management.
- Simple reporting tools.
- GDPR compliance tools.
Pros:
- Affordable and straightforward.
- Excellent customer support.
Cons:
- Limited advanced features.
Ideal For: Small businesses looking for a no-frills CRM.
24. Salesmate CRM
Overview: Salesmate CRM offers sales automation and communication tools for small businesses.
Key Features:
- Built-in calling and texting.
- Customizable sales pipelines.
- Marketing automation.
Pros:
- Affordable pricing.
- User-friendly design.
Cons:
- Limited features for non-sales processes.
Ideal For: Small sales teams needing communication-focused tools.
25. Nutshell CRM
Overview: Nutshell is a user-friendly CRM designed to help small businesses close more deals.
Key Features:
- Sales automation and reporting.
- Pipeline visualization.
- Email marketing tools.
Pros:
- Excellent email marketing integration.
- Simple interface for beginners.
Cons:
- Less customizable than other CRMs.
Ideal For: Small teams focused on sales and email campaigns.
26. NetHunt CRM
Overview: NetHunt CRM integrates directly into Gmail for simplified contact and sales management.
Key Features:
- Email integration and tracking.
- Task and pipeline management.
- Reporting tools within Gmail.
Pros:
- Easy Gmail integration.
- Great for email-centric workflows.
Cons:
- Limited advanced features.
Ideal For: Gmail users who want a simple CRM.
27. OnePageCRM
Overview: OnePageCRM simplifies the sales process by focusing on actionable tasks.
Key Features:
- Task-oriented interface.
- Contact and sales pipeline management.
- Email and call tracking.
Pros:
- Lightweight and action-focused.
- Affordable for small businesses.
Cons:
- Limited features outside of task management.
Ideal For: Small sales teams needing task prioritization.

28. amoCRM
Overview: amoCRM is a sales-focused CRM with advanced messaging integration.
Key Features:
- Multi-channel messaging (email, SMS, chat).
- Visual sales pipelines.
- AI-driven insights and analytics.
Pros:
- Excellent for multi-channel communication.
- Strong automation tools.
Cons:
- Messaging focus may not suit all businesses.
Ideal For: Small businesses with heavy reliance on messaging.
29. Close CRM
Overview: Close CRM is a CRM designed specifically for inside sales teams.
Key Features:
- Built-in calling and email tracking.
- Advanced sales automation.
- Detailed reporting and insights.
Pros:
- Excellent tools for inside sales.
- Highly focused on closing deals.
Cons:
- Less versatile for non-sales processes.
Ideal For: Sales-driven small businesses needing robust tools.
30. Maximizer CRM
Overview: Maximizer CRM is a feature-rich platform offering contact management and business analytics.
Key Features:
- Customizable dashboards.
- Marketing and sales automation.
- Cloud-based and on-premise options.
Pros:
- Strong reporting and analytics tools.
- Flexible deployment options.
Cons:
- Higher price point for advanced features.
Ideal For: Small businesses needing detailed analytics and customization.
Best CRM for Small Business in 2025
These top 30 CRM solutions cater to a variety of needs, industries, and budgets. Whether you’re a startup, a growing small business, or an established company, there’s a CRM that can help you streamline your operations and boost efficiency. Evaluate your business goals, compare features, and select the CRM that aligns best with your needs for 2025.
Comparison Table of Top CRMs
| CRM | Best For | Key Features | Starting Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| HubSpot CRM | Startups | Free plan, contact management | Free |
| Zoho CRM | Growing businesses | AI-driven insights, workflows | $14/user/month |
| Salesforce | Advanced features | Analytics, AppExchange | $25/user/month |
| Freshsales | Simple sales processes | Lead scoring, pipeline management | $15/user/month |
| Monday.com CRM | Flexibility | Customizable workflows | $10/user/month |
How to Choose the Right CRM for Your Business
- Assess Your Needs: Identify what features are most critical for your operations.
- Consider Budget: Look for a solution that fits your financial constraints.
- Evaluate Usability: Ensure the CRM is user-friendly for your team.
- Test Before You Buy: Take advantage of free trials or demo versions.
Implementation Tips
- Train Your Team: Provide resources to help users understand the CRM’s functionality.
- Start with Key Features: Avoid overwhelming your team by focusing on the most critical features first.
- Set Clear Goals: Define metrics to measure the CRM’s impact on your business.
Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a critical process that, when done right, can maximize efficiency and improve customer relationships. Here are some essential tips for successful CRM implementation:
1. Define Clear Objectives
- What to Do: Identify the specific goals you want to achieve with the CRM. Examples include improving sales processes, increasing customer retention, or streamlining workflows.
- Why It Matters: Clear objectives help ensure your CRM implementation is aligned with your business needs and provides measurable outcomes.
2. Choose the Right CRM
- What to Do: Evaluate CRMs based on their features, scalability, cost, and ease of use. Consider integrations with your existing tools (e.g., email, accounting software).
- Why It Matters: Selecting the right CRM ensures it fits your business requirements and avoids complications down the road.
3. Assemble a Dedicated Team
- What to Do: Create a cross-functional team that includes representatives from sales, marketing, customer service, and IT.
- Why It Matters: A collaborative approach ensures all departments’ needs are considered, leading to smoother implementation and adoption.
4. Customize for Your Business
- What to Do: Tailor the CRM’s workflows, fields, and reports to match your specific business processes.
- Why It Matters: Customization increases usability and makes the CRM more relevant to your team’s daily tasks.
5. Clean and Import Data
- What to Do: Audit and clean your existing customer data before migrating it to the new CRM. Remove duplicates and outdated information.
- Why It Matters: Clean data ensures the CRM functions effectively and avoids errors in reporting or automation.
6. Provide Comprehensive Training
- What to Do: Offer training sessions for all team members who will use the CRM. Provide ongoing support and resources, such as user guides and tutorials.
- Why It Matters: Proper training ensures users understand the CRM’s capabilities, increasing adoption and reducing errors.
7. Start Small and Scale Gradually
- What to Do: Begin with a pilot program or roll out the CRM to one department first. Gather feedback before full deployment.
- Why It Matters: A phased approach helps identify potential issues early, making it easier to address them before company-wide implementation.
8. Integrate with Existing Tools
- What to Do: Connect the CRM to your existing systems, such as email platforms, marketing tools, and accounting software.
- Why It Matters: Seamless integration improves efficiency and ensures all your tools work together effectively.
9. Monitor and Measure Performance
- What to Do: Use the CRM’s reporting and analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as lead conversion rates or customer satisfaction.
- Why It Matters: Monitoring performance helps you measure the CRM’s ROI and identify areas for improvement.
10. Gather and Act on Feedback
- What to Do: Regularly collect feedback from users about the CRM’s usability and effectiveness.
- Why It Matters: Continuous feedback allows you to make adjustments, ensuring the CRM continues to meet your team’s needs.
11. Ensure Ongoing Maintenance
- What to Do: Regularly update the CRM software, clean data, and audit workflows.
- Why It Matters: Proper maintenance keeps the CRM running smoothly and ensures it adapts to your business’s evolving needs.
12. Prioritize Security and Compliance
- What to Do: Implement strong access controls, encrypt sensitive data, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
- Why It Matters: Protecting customer data builds trust and prevents legal issues.
13. Leverage Automation Features
- What to Do: Use the CRM’s automation tools for tasks like follow-up emails, lead scoring, and appointment scheduling.
- Why It Matters: Automation saves time and ensures consistent customer interactions.
14. Regularly Review CRM Effectiveness
- What to Do: Schedule periodic reviews of the CRM’s impact on your business processes and objectives.
- Why It Matters: Regular reviews help ensure the CRM continues to deliver value as your business grows.
15. Foster a CRM-First Culture
- What to Do: Encourage your team to rely on the CRM for decision-making and collaboration.
- Why It Matters: A culture that prioritizes the CRM ensures it becomes an integral part of your operations, maximizing its benefits.
Implementing a CRM successfully requires careful planning, collaboration, and ongoing effort. By following these tips, you can ensure a smooth transition and unlock the full potential of your CRM system. Let me know if you’d like additional details or tailored advice for your business!
What are the challenges in CRM?
Implementing and managing a CRM system can significantly improve business processes, but it comes with its share of challenges. Here are some of the common challenges businesses face with CRM systems, along with tips for overcoming them:
1. Low User Adoption Rates
- The Challenge: Employees may resist using the CRM system, either because they find it too complex or don’t see its value.
- Why It Happens: Lack of training, unfamiliarity with the system, or a perception that it adds extra work.
- Solution:
- Provide comprehensive training and ongoing support.
- Demonstrate the CRM’s benefits, such as time savings and better sales tracking.
- Choose a user-friendly CRM with intuitive features.
2. Data Quality Issues
- The Challenge: Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data reduces the effectiveness of the CRM.
- Why It Happens: Poor data entry practices or failure to update records regularly.
- Solution:
- Implement strict data entry guidelines and validation checks.
- Schedule regular data cleaning and audits.
- Use automation tools to minimize manual data entry errors.
3. Integration Difficulties
- The Challenge: Integrating the CRM with existing tools like email, accounting software, or marketing platforms can be complex.
- Why It Happens: Compatibility issues or insufficient IT expertise.
- Solution:
- Choose a CRM that offers pre-built integrations or APIs.
- Work with experienced IT professionals to ensure smooth integration.
- Use middleware solutions to bridge compatibility gaps.
4. High Implementation Costs
- The Challenge: Implementing a CRM system can involve significant upfront costs, especially for small businesses.
- Why It Happens: Licensing fees, training, and customization can add up quickly.
- Solution:
- Start with a scalable, affordable CRM that grows with your business.
- Opt for cloud-based CRMs to reduce infrastructure costs.
- Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to ensure ROI.
5. Customization Complexity
- The Challenge: Customizing the CRM to meet specific business needs can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Why It Happens: Limited technical expertise or overly complex customization requirements.
- Solution:
- Choose a CRM with user-friendly customization options.
- Focus on essential customizations first and expand gradually.
- Consult with CRM vendors or third-party experts for complex requirements.
6. Misalignment with Business Processes
- The Challenge: The CRM doesn’t align well with existing workflows, causing inefficiencies.
- Why It Happens: Poor planning or lack of understanding of business needs.
- Solution:
- Map out your business processes before choosing a CRM.
- Test the CRM during a pilot phase to ensure compatibility.
- Involve stakeholders from all relevant departments during the selection process.
7. Security Concerns
- The Challenge: Protecting sensitive customer data stored in the CRM is critical but challenging.
- Why It Happens: Inadequate security measures or non-compliance with data regulations.
- Solution:
- Choose a CRM with robust security features, such as encryption and role-based access controls.
- Regularly update the system to patch vulnerabilities.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
8. Overwhelming Feature Sets
- The Challenge: Many CRMs come with a wide range of features, which can overwhelm users.
- Why It Happens: Users may not understand how to use all the features effectively.
- Solution:
- Focus on core features during the initial implementation phase.
- Gradually introduce advanced features as users become more comfortable.
- Provide targeted training for specific features.
9. Lack of Clear Objectives
- The Challenge: Without clear goals, businesses struggle to measure the CRM’s effectiveness.
- Why It Happens: Poor planning or lack of understanding of CRM capabilities.
- Solution:
- Define specific, measurable goals for the CRM, such as increasing lead conversion rates or improving customer retention.
- Regularly track and evaluate CRM performance using analytics and reporting tools.
10. Limited Mobile Access
- The Challenge: Field teams or remote workers may find it difficult to access the CRM on the go.
- Why It Happens: Lack of mobile-friendly CRM features.
- Solution:
- Choose a CRM with a robust mobile app.
- Ensure the CRM’s mobile interface is user-friendly and supports offline access.
- Provide training on mobile CRM usage.
11. Over-Reliance on Automation
- The Challenge: Automation can lead to a lack of personal touch in customer interactions.
- Why It Happens: Overuse of automated responses or workflows.
- Solution:
- Use automation for repetitive tasks, but maintain personalized communication for customer-facing interactions.
- Train staff to balance automation with human engagement.
12. Scaling Challenges
- The Challenge: As the business grows, the CRM may struggle to handle increased data and users.
- Why It Happens: The chosen CRM lacks scalability.
- Solution:
- Select a CRM designed to scale with your business.
- Regularly review the system’s capacity and upgrade if necessary.
- Consider cloud-based solutions for easier scalability.
13. Poor Collaboration
- The Challenge: Departments may fail to use the CRM effectively for cross-functional collaboration.
- Why It Happens: Lack of shared processes or inconsistent data entry.
- Solution:
- Train all departments on the CRM’s collaborative features.
- Standardize workflows to ensure consistency.
- Encourage communication and feedback between teams.
14. Insufficient Reporting and Analytics
- The Challenge: Businesses may struggle to generate meaningful insights from the CRM.
- Why It Happens: Limited understanding of reporting tools or insufficient data quality.
- Solution:
- Train users on how to leverage the CRM’s analytics features.
- Ensure data is clean and up-to-date for accurate reporting.
- Customize reports to focus on relevant metrics.
15. Lack of Vendor Support
- The Challenge: Poor support from the CRM vendor can slow down issue resolution and system updates.
- Why It Happens: Vendors may have limited customer service or inadequate resources.
- Solution:
- Research CRM vendors’ support policies before purchasing.
- Choose vendors with positive reviews and responsive support teams.
- Consider working with third-party consultants for additional help.
While CRM systems offer numerous benefits, these challenges can hinder their success if not addressed properly. By planning carefully, providing adequate training, and selecting the right CRM solution, businesses can overcome these obstacles and fully realize the potential of their CRM investments. Let me know if you’d like tailored advice for your specific CRM needs!
Conclusion
The best CRM for small business will depend on your unique needs, industry, and goals. With options ranging from free tools like HubSpot to feature-rich platforms like Salesforce Essentials, there’s a solution for every type of business. Use this guide to evaluate your choices and implement a CRM that drives success in 2025 and beyond.
What are the challenges in CRM?
Implementing a CRM system can improve customer relationships and operational efficiency, but it comes with challenges, such as:
- Low User Adoption Rates: Employees may resist using the CRM if they don’t see its value or find it complex. Address this with proper training and by demonstrating its benefits.
- Data Quality Issues: Incomplete or outdated data can compromise CRM effectiveness. Regular data cleaning and clear data entry protocols are essential.
- Integration Difficulties: Challenges integrating the CRM with existing tools can disrupt workflows. Choose a CRM with pre-built integrations or customizable APIs.
- High Implementation Costs: Licensing, training, and customization expenses can add up. Opt for scalable, cloud-based CRMs to reduce costs.
- Customization Complexity: Overly complex customization may require technical expertise. Start with essential adjustments and consult experts for advanced needs.
- Security Concerns: Protecting sensitive customer data is critical. Implement robust access controls, encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
- Overwhelming Features: Excessive features can confuse users. Focus on core functionalities during the initial phase and introduce advanced features gradually.
Despite these challenges, a well-implemented CRM can streamline workflows, enhance customer interactions, and boost business growth.
Can you provide CRM implementation tips?
Implementing a CRM effectively ensures it becomes a valuable tool for your business. Here are essential tips:
- Define Clear Objectives: Identify specific goals, such as increasing lead conversion rates or improving customer retention.
- Choose the Right CRM: Evaluate CRMs based on features, scalability, cost, and ease of use. Ensure it integrates seamlessly with existing tools.
- Assemble a Dedicated Team: Include representatives from all departments to ensure the CRM meets company-wide needs.
- Clean and Import Data: Audit and organize data before migration to avoid errors and duplication.
- Provide Training: Offer comprehensive training and ongoing support to ensure user adoption and proficiency.
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot program or roll out the CRM to a single department. Use feedback to refine processes.
- Leverage Automation: Use automation for repetitive tasks like email follow-ups and data entry to save time.
- Monitor and Measure: Regularly review CRM performance and its impact on business objectives.
- Ensure Security: Implement strong access controls, encryption, and compliance with data protection laws.
- Foster a CRM-First Culture: Encourage teams to rely on the CRM for decision-making and collaboration.
These steps will help ensure your CRM implementation is smooth and successful, delivering measurable results for your business. Let me know if you need further assistance with these topics!

What are the challenges in CRM?
Implementing and using a CRM system can present several challenges:
- Low User Adoption: Employees may resist using the CRM due to complexity or lack of training. Address this with clear demonstrations of its benefits and comprehensive training.
- Poor Data Quality: Inaccurate, duplicate, or outdated data can undermine the CRM’s effectiveness. Regularly clean and audit your data to maintain accuracy.
- Integration Issues: Ensuring the CRM works seamlessly with other tools like email, marketing platforms, and accounting systems can be challenging. Choose CRMs with robust integration options or customizable APIs.
- High Costs: CRM systems can be expensive to implement, particularly for small businesses. Opt for scalable, cloud-based CRMs that grow with your needs.
- Customization Complexity: Tailoring the CRM to fit specific business processes can require technical expertise. Focus on essential features first and seek expert advice for advanced customizations.
- Security Risks: Protecting customer data is crucial. Implement strong access controls, data encryption, and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
- Feature Overload: Some CRMs come with too many features, which can overwhelm users. Start with core functionalities and gradually introduce additional features.
While these challenges exist, they can be mitigated through careful planning, proper training, and selecting the right CRM for your business needs.

Can you provide CRM implementation tips?
Successfully implementing a CRM requires strategic planning and execution. Here are some tips:
- Define Goals: Clearly outline what you want to achieve with the CRM, such as improving sales tracking, customer retention, or operational efficiency.
- Choose the Right CRM: Evaluate options based on your budget, scalability, and required features. Ensure it integrates with your existing tools.
- Clean Data Before Migration: Audit, clean, and organize your data to avoid errors during migration.
- Provide Training: Educate your team on how to use the CRM effectively. Include tutorials, user guides, and hands-on training sessions.
- Start Small: Roll out the CRM in one department or with a specific feature set to gather feedback and refine processes.
- Leverage Automation: Use the CRM’s automation features to handle repetitive tasks, such as email campaigns, task assignments, and data updates.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly track KPIs like lead conversion rates and sales cycle durations to measure the CRM’s impact.
- Foster Adoption: Encourage employees to use the CRM consistently by showing them how it benefits their roles.
- Ensure Security: Protect sensitive data with role-based access controls, encryption, and compliance with legal standards.
- Seek Feedback and Improve: Collect user feedback regularly to identify pain points and improve the system.
By following these tips, your CRM implementation will be smoother and more likely to achieve the desired outcomes for your business. Let me know if you’d like additional guidance!
What are the challenges in CRM?
Implementing and managing a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system can bring immense benefits to businesses, but it is not without its challenges. Here’s a detailed exploration of these challenges and actionable ways to address them:
1. User Adoption Resistance
Challenge: Employees may resist using a CRM system due to unfamiliarity, perceived complexity, or fear of change.
Why It Matters: A CRM is only as effective as its users’ willingness to embrace and utilize it fully.
Solution:
- Provide comprehensive training and demonstrations to show how the CRM can simplify their daily tasks.
- Involve end-users in the selection process to ensure the system meets their needs.
- Gamify CRM adoption by setting goals and rewarding employees for active usage.
2. Poor Data Quality
Challenge: Inconsistent, outdated, or duplicate data reduces the value of CRM insights.
Why It Matters: Poor data leads to unreliable reports, ineffective campaigns, and wasted resources.
Solution:
- Implement strict data entry protocols and validation rules to ensure consistency.
- Schedule regular data audits to clean and update records.
- Use automation tools to minimize human error during data entry.
3. Integration Difficulties
Challenge: CRMs often need to connect with existing systems like email platforms, marketing tools, and accounting software. Integration issues can lead to inefficiencies.
Why It Matters: Without seamless integration, you may face data silos and duplicative work.
Solution:
- Select a CRM with robust built-in integrations or APIs for customization.
- Engage IT experts to facilitate smooth integration with existing tools.
- Test integrations during a pilot phase before full implementation.
4. High Costs and Budget Constraints
Challenge: Implementing a CRM involves upfront costs, including licensing, training, and customization.
Why It Matters: For small businesses, these costs can strain budgets and lead to underutilization.
Solution:
- Opt for affordable, cloud-based CRMs with scalable pricing models.
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to justify the investment.
- Start with essential features and expand as your budget allows.
5. Security and Compliance Risks
Challenge: Storing sensitive customer data in a CRM poses potential risks if not properly secured.
Why It Matters: Data breaches can damage customer trust and lead to legal repercussions.
Solution:
- Choose a CRM with advanced security features like encryption and role-based access controls.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA.
- Regularly review and update security protocols.
6. Overwhelming Feature Sets
Challenge: Many CRMs come with an extensive range of features, which can overwhelm users and complicate adoption.
Why It Matters: Users may not utilize key features, leading to a poor return on investment.
Solution:
- Start by focusing on core features relevant to your business.
- Provide targeted training on advanced features after the initial rollout.
- Customize the interface to simplify workflows.
7. Scalability Challenges
Challenge: As businesses grow, their CRM needs evolve. An initially suitable system may struggle to scale with increased data and users.
Why It Matters: Switching CRMs mid-growth can disrupt operations.
Solution:
- Choose a scalable CRM that can handle future growth.
- Periodically review the CRM’s performance and upgrade plans as needed.
By anticipating these challenges and proactively addressing them, businesses can maximize the benefits of their CRM systems and achieve long-term success.
Can you provide CRM implementation tips?
Implementing a CRM system is a significant step for any business. Proper implementation ensures the system aligns with your goals, engages your team, and delivers measurable value. Here’s how to make the process seamless and effective:
1. Clearly Define Objectives
Tip: Identify specific goals for the CRM, such as improving lead conversion rates, tracking sales pipelines, or enhancing customer retention.
Why It Adds Value: Clear objectives ensure the CRM implementation is purpose-driven and measurable.
2. Choose the Right CRM for Your Needs
Tip: Evaluate CRMs based on features, scalability, ease of use, and cost. Consider industry-specific tools if applicable.
Why It Adds Value: Selecting the right CRM reduces the risk of dissatisfaction and reimplementation costs later.
3. Involve Stakeholders
Tip: Engage employees from sales, marketing, customer service, and IT in the decision-making and implementation process.
Why It Adds Value: Inclusive planning ensures the CRM meets the needs of all departments and fosters early buy-in.
4. Clean and Organize Data
Tip: Before migrating data to the CRM, remove duplicates, outdated information, and incomplete records.
Why It Adds Value: Clean data ensures accurate reporting and smoother system operation.
5. Customize the CRM
Tip: Tailor the CRM’s workflows, fields, and dashboards to align with your business processes.
Why It Adds Value: Customization improves usability and relevance, making it easier for employees to integrate the CRM into their daily routines.
6. Provide Comprehensive Training
Tip: Offer training sessions for all users and provide access to ongoing resources like tutorials and FAQs.
Why It Adds Value: Knowledgeable users are more likely to adopt the system fully and utilize advanced features.
7. Roll Out in Phases
Tip: Start with a pilot phase, deploying the CRM in one department or with limited features. Gather feedback and refine processes before full implementation.
Why It Adds Value: A phased rollout minimizes disruptions and allows for adjustments based on real-world usage.
8. Leverage Automation
Tip: Use the CRM’s automation tools for repetitive tasks like lead follow-ups, email campaigns, and data updates.
Why It Adds Value: Automation saves time and ensures consistent execution of critical tasks.
9. Monitor and Measure Performance
Tip: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like sales cycle duration, customer satisfaction, and conversion rates to measure the CRM’s impact.
Why It Adds Value: Continuous monitoring ensures the CRM is meeting its objectives and provides insights for improvement.
10. Ensure Ongoing Maintenance
Tip: Regularly update the CRM software, clean data, and review workflows to keep the system optimized.
Why It Adds Value: Maintenance prevents issues and ensures the CRM evolves with your business needs.
11. Foster a CRM-First Culture
Tip: Encourage employees to rely on the CRM for decision-making and collaboration. Set expectations for its use across the organization.
Why It Adds Value: A CRM-first culture maximizes the system’s potential and ensures company-wide consistency.
By following these tips, businesses can ensure their CRM implementation is successful, maximizing the system’s potential to drive growth, enhance customer relationships, and streamline operations. Let me know if you need further guidance or tailored strategies!
Final Thoughts and Best Recommendations
CRM systems are essential tools for businesses of all sizes, offering opportunities to improve customer relationships, streamline operations, and boost revenue. However, challenges like user adoption, data quality, integration, and costs must be addressed strategically for successful implementation and long-term benefits.
Best Recommendations for Businesses
- Choose a Scalable CRM: Select a system that can grow with your business. For startups and small businesses, HubSpot CRM offers a free plan with robust features, while Zoho CRM provides affordable customization for scaling.
- Focus on Usability: Ensure the CRM is intuitive and easy for your team to adopt. Pipedrive and Monday.com CRM are excellent options with user-friendly interfaces.
- Embrace Automation: Look for CRMs with built-in automation to save time and reduce human error. ActiveCampaign excels in marketing automation, and Freshsales offers automation for sales processes.
- Leverage Integrations: Choose a CRM that integrates seamlessly with your existing tools. For businesses using Google Workspace, Copper CRM is highly recommended.
- Prioritize Security and Compliance: Ensure your CRM has advanced security features like encryption and role-based access controls. For industries with strict compliance needs, Salesforce Essentials and SugarCRM are excellent choices.
- Start Small: Begin with essential features and expand as your team grows more comfortable. Use pilot programs to gather feedback and refine the system before full deployment.
Conclusion
A well-implemented CRM system can be a game-changer for your business, improving customer satisfaction, increasing sales efficiency, and providing actionable insights. By carefully selecting a CRM that aligns with your business needs, addressing potential challenges proactively, and focusing on usability and integration, you can ensure a successful implementation that delivers measurable ROI.
Among the top choices, HubSpot CRM stands out as a versatile and budget-friendly option, while Salesforce Essentials is ideal for businesses seeking advanced customization and analytics. Ultimately, the best CRM is the one that fits your specific business goals and empowers your team to build stronger customer relationships.
Take the time to evaluate, implement, and maintain your CRM system carefully—it’s an investment in the long-term growth and efficiency of your business.